Microorganisms are called “invisible majority” that run the biosphere and run the world. They are on and in the depth of the seas, oceans, and earth. They are found in the hottest and the coldest places and can survive and reproduce in the harshest environments. They are about 3.5 billion years old with a very elaborate and complex communication system called quorum sensing and organizational capability such as biofilm formation to combat environmental stress such as our sanitizers. Just recently we recognized a new domain called Archaea, so now we talk about three domains: Bacteria, and Archaea (both prokaryotes) and the rest of the living beings as Eukaryotes.
The vast majority of microorganisms can not be cultured (almost 99%) in the lab using culture methods; they are known as “Microbial Dark Matter”. Omics are here to help. In the food industry, food safety hazards must be controlled and almost 88% of the recalls in the United states are due to Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp and undeclared allergens. The space age and travel to the moon necessitated a solid, scientifically- based food safety management system for space travelers. NASA and others started using a management system called Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP).
Today HACCP is recognized, accepted and used by governments, academia and food industry nationally and globally. On January 4, 2011, the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) introduced seven foundational rules that essentially used the HACCP principles to ensure safety of food for humans, foods for animals, produce safety, safety of the imported food, food defense, and transportation.
Just imagine combining all we have learned from HACCP and FSMA and combining them with the greatest revolution in biological, microbiological, and other biotechnological sciences and technologies ; it is known as the OMICS REVOLUTION. This course is the first of its kind (www.foodsafetyomics.us) in the world and is about the application of genomics, metagenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microbiomics, allergenomics and other omics (multi-omics) in food safety.
The first half of the course is about explaining different omics and food safety, and the second half is how to write a HACCP Plan or Food Safety Plan using omics principles.

Option One-
On Zoom and Instructor-Led – Can also be arranged upon request
2024
November 1, 2024, 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM – EST
November 2, 2024, 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM – EST
2025 Classes
March 19, 20 2025 – EST
June 26, 27, 2025 – PST
Table of Contents
Preface
References and Resources
Module 1. History from the First Microbe to the First Sequencing of DNA, RNA and Proteins
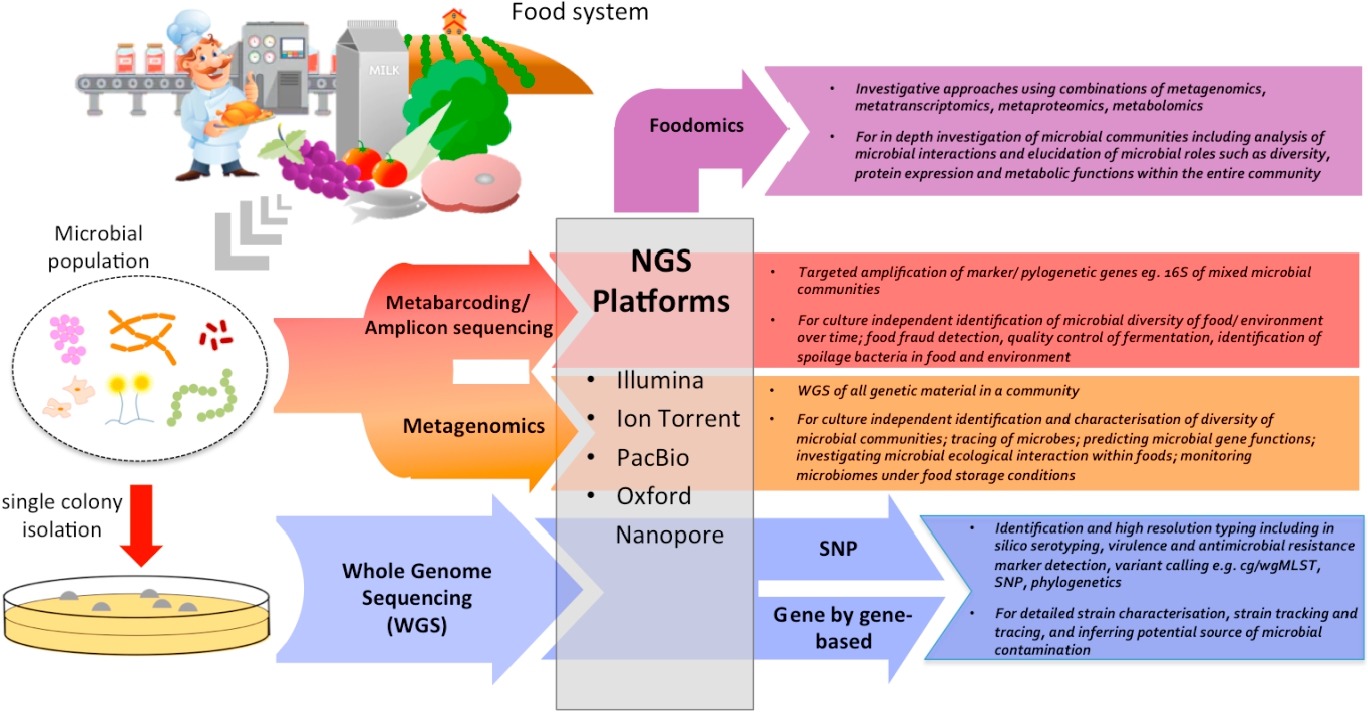
Module 2. Overview of Genomics, Metagenomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, Microbiomics, Allergenomics, other Omics (multi-omics) and Food Safety
Module 3. DNA, Genomics, Metagenomics and Food Safety
Module 4. The FDA and USDA Whole Genome Sequencing, FDA GenomeTrakr and GalaxyTrakr
Module 5. RNA, Transcriptomics, Meta-transcriptomics and Food Safety
Module 6. Protein, Proteomics, Meta-proteomics and Food Safety
Module 7. Allergens, Allergenomics, Meta-Allergenomics and Food Safety
Module 8. Metabolites, Metabolomics and Food Safety
Module 9. Next Generation Sequencing and Food Safety
Module 10. Bioinformatics, Food Informatics, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning
and Food Safety
Module 11. Microbiological Food Safety Hazards, Microbiome and Microbiomics
Module 12. Chemical Food Safety Hazards Control, Cheminformatics and Hurdle Technologies
Module 13. HACCP – Multi-omics – Prerequisite Programs
Module 14. HACCP – Multi-omics – Preliminary Steps
Module 15. The First Principle of HACCP – Conduct a Hazard Analysis – Using Multi-omics
Module 16. The Second Principle of HACCP – Determine Critical Control Points – Using Multi-Omics
Module 17. The Third Principle of HACCP – Determine Critical Limits – Using Multi-Omics
Module 18. The Fourth Principle of HACCP – Establish Monitoring Procedures – Using Multi-Omics
Module 19. The Fifth Principle of HACCP – Establish Corrective Actions – Using Multi-Omics
Module 20. Th Sixth Principle of HACCP – Establish Verification Procedures – Using Multi-Omics Documentation Procedures
Module 21 – The Seventh Principle of HACCP – Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation Procedures – Using Multi-Omics
Module 22. Development, Implementation, Maintenance and Assessment of the HACCP System


Option Two-
Self-Paced,
to be completed within 60 Days
Table of Contents
Preface
References and Resources
Module 1. History from the First Microbe to the First Sequencing of DNA, RNA and Proteins
Module 2. Overview of Genomics, Metagenomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, Microbiomics, Allergenomics, other Omics (multi-omics) and Food Safety
Module 3. DNA, Genomics, Metagenomics and Food Safety
Module 4. The FDA and USDA Whole Genome Sequencing, FDA GenomeTrakr and GalaxyTrakr
Module 5. RNA, Transcriptomics, Meta-transcriptomics and Food Safety
Module 6. Protein, Proteomics, Meta-proteomics and Food Safety
Module 7. Allergens, Allergenomics, Meta-Allergenomics and Food Safety
Module 8. Metabolites, Metabolomics and Food Safety
Module 9. Next Generation Sequencing and Food Safety
Module 10. Bioinformatics, Food Informatics, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning
and Food Safety
Module 11. Microbiological Food Safety Hazards, Microbiome and Microbiomics
Module 12. Chemical Food Safety Hazards Control, Cheminformatics and Hurdle Technologies
Module 13. HACCP – Multi-omics – Prerequisite Programs
Module 14. HACCP – Multi-omics – Preliminary Steps
Module 15. The First Principle of HACCP – Conduct a Hazard Analysis – Using Multi-omics
Module 16. The Second Principle of HACCP – Determine Critical Control Points – Using Multi-Omics
Module 17. The Third Principle of HACCP – Determine Critical Limits – Using Multi-Omics
Module 18. The Fourth Principle of HACCP – Establish Monitoring Procedures – Using Multi-Omics
Module 19. The Fifth Principle of HACCP – Establish Corrective Actions – Using Multi-Omics
Module 20. Th Sixth Principle of HACCP – Establish Verification Procedures – Using Multi-Omics Documentation Procedures
Module 21 – The Seventh Principle of HACCP – Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation Procedures – Using Multi-Omics
Module 22. Development, Implementation, Maintenance and Assessment of the HACCP System


Option Three –
This course can be offered on your site or In Hermosa Beach, California,
1250 Pacific Coast Highway. Please contact Alex
Phone: 310-694-1544
Email: alexkashef@geosda.com
Table of Contents
Preface
References and Resources
Module 1. History from the First Microbe to the First Sequencing of DNA, RNA and Proteins
Module 2. Overview of Genomics, Metagenomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, Microbiomics, Allergenomics, other Omics (multi-omics) and Food Safety
Module 3. DNA, Genomics, Metagenomics and Food Safety
Module 4. The FDA and USDA Whole Genome Sequencing, FDA GenomeTrakr and GalaxyTrakr
Module 5. RNA, Transcriptomics, Meta-transcriptomics and Food Safety
Module 6. Protein, Proteomics, Meta-proteomics and Food Safety
Module 7. Allergens, Allergenomics, Meta-Allergenomics and Food Safety
Module 8. Metabolites, Metabolomics and Food Safety
Module 9. Next Generation Sequencing and Food Safety
Module 10. Bioinformatics, Food Informatics, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning
and Food Safety
Module 11. Microbiological Food Safety Hazards, Microbiome and Microbiomics
Module 12. Chemical Food Safety Hazards Control, Cheminformatics and Hurdle Technologies
Module 13. HACCP – Multi-omics – Prerequisite Programs
Module 14. HACCP – Multi-omics – Preliminary Steps
Module 15. The First Principle of HACCP – Conduct a Hazard Analysis – Using Multi-omics
Module 16. The Second Principle of HACCP – Determine Critical Control Points – Using Multi-Omics
Module 17. The Third Principle of HACCP – Determine Critical Limits – Using Multi-Omics
Module 18. The Fourth Principle of HACCP – Establish Monitoring Procedures – Using Multi-Omics
Module 19. The Fifth Principle of HACCP – Establish Corrective Actions – Using Multi-Omics
Module 20. Th Sixth Principle of HACCP – Establish Verification Procedures – Using Multi-Omics Documentation Procedures
Module 21 – The Seventh Principle of HACCP – Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation Procedures – Using Multi-Omics
Module 22. Development, Implementation, Maintenance and Assessment of the HACCP System



